In C programming languages, a data type tells to the compiler about which the type of data is going to be stored and the compiler reserves the fixed number of bytes for that particular data (i.e. variable or constant).
we can say that, a data type defines two things:
- Type of data (i.e. Primary (int,char,float & void) ,
derived ( i.e. Array, function & pointer) , User define (i.e.
structure, union & enum)
- Memory blocks to be reserved for the data.
Data types are classified in
three types i.e. Primary data type, derived data type & User
define data type.
Units of Memory
0 or 1 – 1 bit
Group of 4 bits = 1 nibble
Group of 8 bits = 1 bytes
·
Primary Data types:
There are 4 primary or basic
data types in C.
1) Integer type:
§ It contains integer numbers.
§ To represent integer data
type we use int keyword in C.
|
Sr. No. |
Data Type |
Size in Memory |
Keyword |
Format Specifier |
Range |
|
1 |
integer or sign integer |
2 Bytes |
int |
%d |
-32768 to 32767 |
|
2 |
Unsigned integer |
2 Bytes |
unsigned |
%u |
0 to 65535 |
|
3 |
Short integer |
1 Byte |
short int (or short ) |
%hd |
-128 to 127 |
|
4 |
Unsigned short integer |
1 Byte |
unsigned short |
%hu |
0 to 255 |
|
5 |
long integer or Sign long integer |
4 Bytes |
long int (or long) |
%ld |
-2,147,483,648 to
2,147,483,647 |
|
6 |
Unsigned long integer |
4 Bytes |
unsigned long int (or unsigned
long) |
%lu |
0 to 4,294,967,295 |
1) Floating type:
§ Floating type contains decimal point (fractional numbers)
§ Floating point data type
stored in 4 byte (32 bit) memory with 6 digit precision.
§ In float number after point numbers of digit is present is
called precision
|
Sr. No. |
Data Type |
Size in Memory |
Format Specifier |
Range |
|
1 |
float |
4 Bytes |
%f |
3.4 e -38 to 3.4 e +38 |
|
2 |
double |
8 Bytes |
%lf |
1.7 e -308 to 1.7 e +308 |
|
3 |
long double |
10 Byte |
%Lf |
3.4 e -4932 to 1.1 e +4932 |
2) Character data type:
§ Character type is define as
a char
|
Sr. No. |
Data Type |
Size in Memory |
Format Specifier |
Range |
|
1 |
char or signed char |
1Bytes |
%c |
-128 to 127 |
|
2 |
char or unsigned char |
1 Bytes |
%c |
0 to 255 |
Note – empty data type is called void data
----------------------------------------------------------
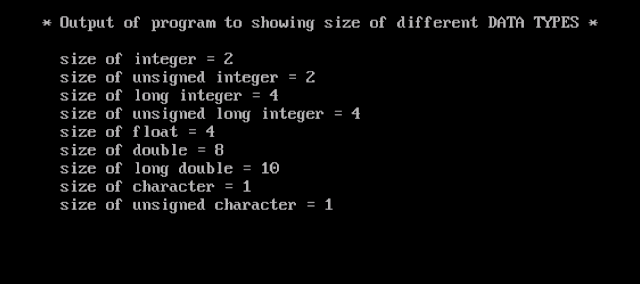
// Program to showing size of different DATA TYPES
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
clrscr();
printf("\n
* Output of program to showing size of different DATA TYPES *\n");
printf("\n size of integer = %d",sizeof(int));
printf("\n size of unsigned integer =
%d",sizeof(unsigned));
printf("\n size of long integer =
%d",sizeof(long));
printf("\n size of unsigned long integer =
%d",sizeof(unsigned long));
printf("\n size of float = %d",sizeof(float));
printf("\n size of double = %d",sizeof(double));
printf("\n size of long double = %d",sizeof(long
double));
printf("\n size of character = %d",sizeof(char));
printf("\n size of unsigned character =
%d",sizeof(unsigned char));
getch();
}
·
Derived data type
1) Array:
§ Collection of similar data
type is called array.
2) Function:
§ Outside of main function
subprogram is written is called function.
3) Pointer:
§ Pointer is variable which
holds address of another variable.
·
User define data type
1) Structure / Union :
§ It is collection of
different data type.
2) Enum :
Enum
(or Enumeration) is used to assign names to integral constants.








0 Comments