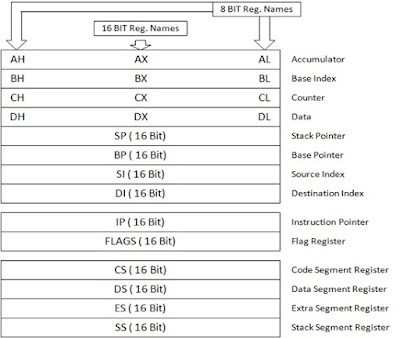
Programming Model or Register Organization of 8086 Microprocessor
Fig. : Register Organization of 8086 Microprocessor
1) General purpose
register:
8086 microprocessor contains 8 general purpose
register, which are used to store data temporarily. These register are AH, AL,
BH, BL, CH, CL, DH& DL. All registers are 8 bit register. It means that
they can store 8 bit data to store 16 bit data these registers are combined as
follows.
AX (16) =AH (8) +AL (8)
BX (16) =BH (8) +BL (8)
CX (16) =CH (8) +CL (8)
DX (16) =DH (8) +DL (8)
These
registers are programmable registers. It means that users can read & write
data into these registers and they can be overwritten by users.
2) Pointing and Index register:
There
are 2 pointing and 2 index registers in 8086 up. The two pointing registers are
sp (stack pointer), & BP (Base Pointer). These registers are used to store
16bit offset address of data in memory.
The
SP is used to store offset address of data stored in stack segment of memory.
BP is also used to store offset address of data stored in stack segment of
memory. The difference between these two are that SP stores TOP data’s offset
address and BP stores Bottom data’s offset address.
The
2 index register SI (source index) & DI (destination index). These two
16-bit register are used to point towards data stored in either data segment
(DS) or in extra segment (ES) of memory.
3) Instruction pointer (IP):
This
16 bit register is use to point towards an instruction stored in code segment
of memory.
4) Segment Register:
The
8086 microprocessor can address up to 1MB of memory. To access (read/write) the
memory and I/O devices 8086 sends 20 bit physical address. The memory of 8086
is divided into 4 segments i.e. code segment, data segment, extra segment
&stack segment. Each segment is of 64K bytes in size. The 4 segment
register of 16 bits in BIU are used to store base address for respective
segments. The 20 bit physical address is calculated by adding two 16 bit
addresses i.e. base address & offset address.
5) Flag Register:
8086
microprocessor contains a 16 bit flag register. Out of this 16 bit only 9 flags
are active (used). The 9 flags are classified into two types.
A] Conditional
Flag: i.e.
carry flag, Auxilary carry flag, sign flag, zero flag, polarity flag, overflow
flag.
B] Control Flag: Interrupt flag, Trap
flag, directions flag.






0 Comments